Calibration Protocols for Laboratory Balances: Best Practices
Accurate weighing is fundamental to countless scientific endeavours. In a laboratory setting, ensuring the precision of your measurements relies heavily on properly calibrated balances. This blog post will guide you through the best practices for calibrating and maintaining your laboratory balances for optimal accuracy.

Understanding Calibration
Calibration is the process of verifying and adjusting a measuring instrument to ensure its readings align with known standards. Regular calibration is crucial for laboratory balances as even minor deviations can significantly impact your results.
Frequency of Calibration
The frequency of calibration depends on several factors, including:
- Balance Type: Analytical balances, used for highly precise measurements, require more frequent calibration compared to top-loading balances.
- Usage Frequency: Regularly used balances need calibration more often than those used infrequently.
- Required Accuracy: If your work demands extremely high precision, you might need more frequent calibrations.
A good rule of thumb is to consult the manufacturer’s recommendations and establish a routine calibration schedule. Generally, calibrations are recommended every 6 months to a year. However, some balances may require more frequent adjustments.
Preparing for Calibration
Before calibration, ensure your balance is in optimal condition:
- Cleanliness: Remove any dirt or debris from the weighing pan and surrounding areas.
- Levelling: If your balance has a level indicator, use it to ensure the balance is level for accurate readings.
- Environmental Factors: Place the balance on a stable surface in a location free from drafts, vibrations, and extreme temperature fluctuations.
- Warm-up Time: Allow the balance to warm up for at least 30 minutes before calibration to ensure internal electronics have stabilised.
Calibration Procedure (General Guidelines)
It’s important to note that specific calibration procedures will vary depending on your balance model. Always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for detailed steps.
Here’s a general outline of the calibration process:
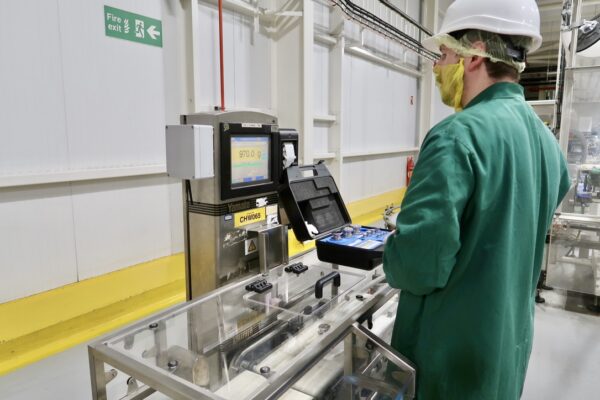
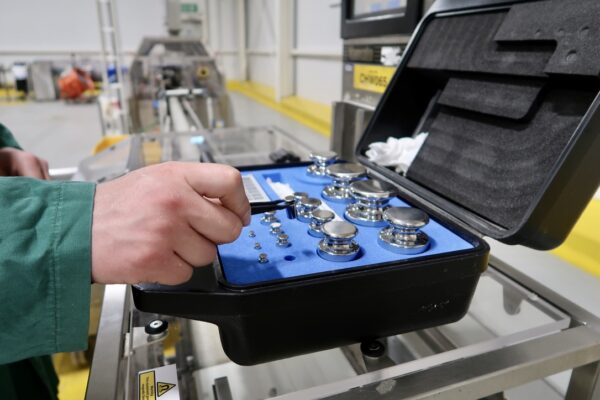
- Gather Calibration Weights: Use certified calibration weights with a known mass that covers the weighing range you typically use.
- Access Calibration Mode: Consult your manual for instructions on entering the calibration mode on your specific balance.
- Place Calibration Weight: Carefully place the first calibration weight on the centre of the pan and record the displayed weight.
- Adjustment (if applicable): If there’s a discrepancy between the displayed weight and the weight of the calibration weight, some balances allow for internal adjustments. Refer to the manual for calibration adjustment procedures specific to your model.
- Repeat for Each Weight: Repeat steps 3 and 4 for each calibration weight you’re using.
- Exit Calibration Mode: Once all weights have been used, follow the manufacturer’s instructions to exit calibration mode.
Maintaining Accuracy Between Calibrations
- Regular Cleaning: Maintain a clean working environment and regularly clean the balance pan and weighing chamber.
- Careful Handling: Avoid overloading the balance or exposing it to shocks and vibrations.
- Environmental Control: Keep the balance in a stable environment with minimal drafts and temperature fluctuations.
- Calibration Records: Maintain records of calibration dates, weights used, and any adjustments made.
Additional Considerations
- Internal vs. External Calibration: Some balances have internal calibration features, while others require external calibration weights. Determine the type of calibration your balance requires.
- Accredited Calibration Services: For critical applications demanding the highest level of accuracy, consider accredited calibration services from a qualified provider. Companies such as MWS can provide traceable calibration services to ensure your equipment is meeting stringent guidelines and is operating to its full potential.
By following these best practices, you can ensure your laboratory balances maintain optimal accuracy, leading to reliable and trustworthy results in your operations.